What is Storage Virtualization in Cloud Computing?
Storage Virtualization in cloud computing is the division of the actual storage into different storage devices/devices, giving the impression of being a single storage device/device. That is also known as a group of accessible storage devices only monitored from intermediate backups. This Virtualization has many advantages, such as easy backup, access, and data restoration. In addition, the entire process takes very little time and works efficiently. However, storage virtualization in cloud computing needs to reflect the true complexity of storage area networks (SANs).
This virtualization applies to all SAN levels. For example, Storage Virtualization in cloud computing contributes to location independence by using the physical location of data. This system provides customers with storage space to store their data and takes over the mapping process. In addition, the output of virtualization can cascade as input to higher levels of virtualization.
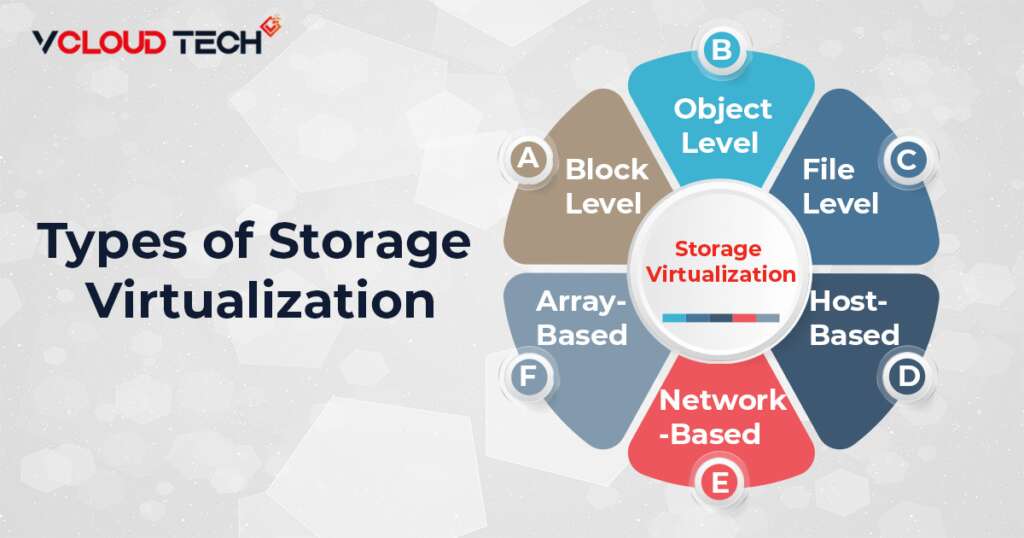
Types of Storage Virtualization:
Here, we will list down all the storage virtualization in Cloud Computing.
- Block Level
- Object Level
- File Level
- Host-Based
- Network-Based
- Array-Based
Block Level:
When writing to the hard drive of a desktop computer, block-level storage uses because it writes directly to the hard drive. With virtualized block storage, your server functions as a desktop computer, with access to a virtual drive that behaves like a regular hard drive. That provides benefits such as booting from block devices and improved performance and scalability.
Object Level:
Object Storage does not store data directly on disk. Instead, the application accesses this data through API calls. That is a more scalable solution than block storage for large amounts of data. In addition, that means you don’t have to worry about running out of space after setting up your bucket.
File Level:
If a user wants to host files on another server, the user uses his server software, such as Samba or NFS. Files are in folders called shares. That eliminates the need to manage storage space and allows multiple users to share storage devices. Servers, virtual servers, and desktop computers can fully utilize file servers.
Host-Based:
Virtual servers typically do not directly access the host machine’s drives. That is to increase security by isolating the host from the guests. This way, even if the guest is hacked or infected, it cannot spread to the host or Virtual Machines. However, some users prefer to avoid this separation. Instead, Host-based storage virtualization allows access to hosts or devices attached to hosts. The server installs a driver that intercepts and redirects IO requests (input and output). Usually, these IO requests go directly to the hard drive but sometimes to other devices such as hard drives. For example, you can transfer a USB flash drive. The most common use for this type of storage is to access physical installation CDs or DVDs so that operating systems can easily install them in virtual machines.
Network-Based:
Place a Fiber Channel switch between the host and the storage. The control is where virtualization takes place and redirects IO requests. This method works on any operating system without special drivers.
Array-Based:
The master array handles all IO requests for all collections. That enables management from a central location and simplifies data migration.
Methods of Storage Virtualization:
File-Based Storage Virtualization:
This virtualization is purpose-built and can use for NAS (Network-Attached Storage) systems. File-based storage virtualization in cloud computing uses Server Message Blocks or Network File System protocols and uses them to remove the dependencies of typical network-attached storage arrays. That occurs between the data accessed and its physical store location. It also has the added benefit of better handling of file migrations in the background, resulting in better performance.
Block-Based Virtual Memory:
Block-based virtual memory is more commonly used than virtual memory systems because virtual memory systems use for specific purposes. Block-based virtual storage systems use logical storage, such as drive partitions, from physical storage within storage devices. It also abstracts logical storage, such as hard disk drives and solid-state storage devices. That also allows Virtualization Management Software to learn about available device capacity and divide it into shared resources.
Why is Storage Virtualization Important?
Task Execution:
Storage virtualization appliances are responsible for multiple tasks, such as heterogeneous replication and federation. These devices are placed in front of the array and form a standard interface for the host. That allows administrators to mix and match protocols and displays behind the appliance.
WAN Management:
Multiple copies of similar data are not sent over WAN. Data is buffered and sent at LAN speed with the help of a WAN accelerator, which doesn’t impact WAN performance.
Disaster Recovery:
Storage virtualization in cloud computing increases disk utilization and flexibility. That improves disaster recovery and business continuity.
Storage Tiering:
Storage tiering is the practice of monitoring and selecting the most frequently used data and placing it in the highest-performing storage pools. The least frequently used data is in the lowest-performing storage pool.
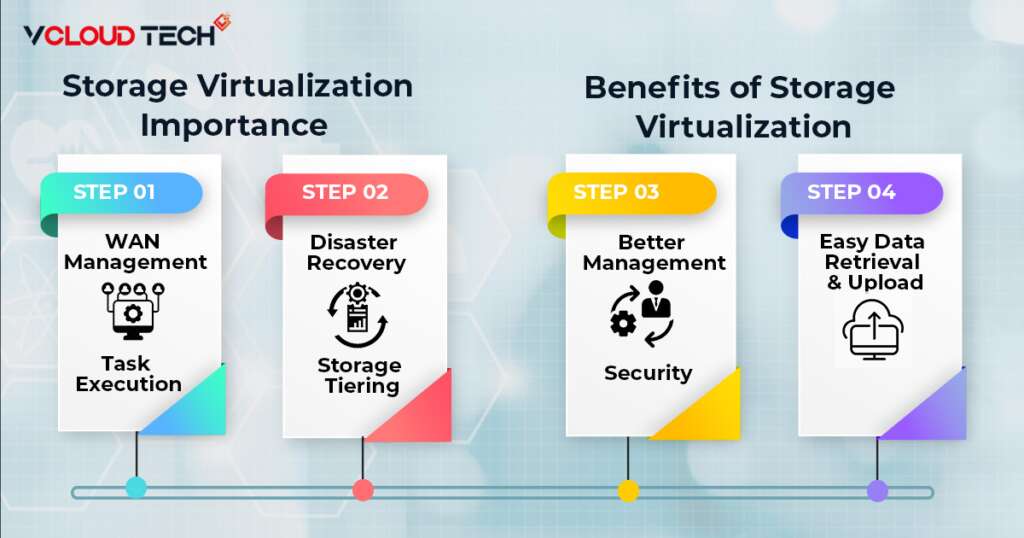
Benefits of Storage Virtualization:
Learn about the benefits of storage virtualization in cloud computing.
Easy Data Retrieval and Upload:
With storage virtualization, quickly retrieve data from Virtual Storage. It’s as easy as accessing files on your local computer. Saving information is very easy with the help of an application and an internet connection. That is a simple task.
Better Management:
Data can be migrated based on usage. For instance, a robust storage system can store frequently used data. However, rarely used data stores on slightly slower systems. That is an example of a battery management system; our customers have no storage issues.
Security:
With Storage Virtualization, Store data in various locations with maximum protection. In a disaster, data can retrieve from another site without affecting customers. In addition, security can meet actual usage needs instead of providing additional storage space.
Reach out to us and book a Free Consultation with vCloud Tech or chat with one of our representatives. Connect with us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn for more information.









