IT asset management (ITAM) encompasses the comprehensive tracking and management of IT assets, ensuring their proper utilization, maintenance, upgrades, and end-of-life disposal. It involves leveraging financial, contractual, and inventory data to monitor and make strategic decisions regarding IT assets. The primary objective is to ensure the efficient and effective utilization of IT resources. ITAM also aids in cost optimization by reducing the overall number of assets in use and prolonging their lifespan, thus avoiding expensive upgrades. A crucial aspect of IT Asset Management (ITAM) is understanding the total cost of ownership and identifying opportunities for optimizing asset usage.
What is an IT Asset?
An IT asset refers to any information, software, or hardware utilized by an organization in its business operations. Hardware assets encompass tangible computing equipment like physical servers located in data centers, desktop computers, mobile devices, laptops, keyboards, and printers. Software assets include applications for which licenses are typically issued per user or machine, as well as software systems and databases developed using open-source resources. Cloud-based assets, such as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications, also fall within the scope of software assets.
How does an IT Asset Management Process Work?
IT asset management (ITAM) is a systematic approach to managing an organization’s IT assets throughout their lifecycle. The process involves acquiring, deploying, tracking, maintaining, and disposing of IT assets in an efficient and cost-effective manner. Here’s an overview of how an IT asset management process typically works:
Planning:
The process begins with defining the goals and objectives of IT asset management. This includes determining the scope of assets to be managed, establishing policies and procedures, and identifying the resources required for effective management.
Asset Identification:
All IT assets within the organization are identified and categorized using tools like SolarWinds IT Asset Management. This includes hardware (computers, servers, networking equipment), software (licenses, applications), and other digital assets.
Asset Acquisition:
IT assets are acquired based on predefined requirements and procurement processes. This involves evaluating vendors, negotiating contracts, and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.

Asset Deployment:
Once the assets are acquired, they are deployed to the appropriate users or locations. This may involve installing software, configuring hardware, and connecting devices to the network.
Asset Tracking:
A central repository, such as Alloy IT Asset Management Software or any other IT Asset Management Tracking Software, is used to track each asset’s location, ownership, and status. This includes recording asset details, purchase dates, warranty information, and maintenance history.
Asset Maintenance:
Regular maintenance activities, such as software updates, hardware repairs, and license renewals, are performed to ensure optimal performance and compliance. This may involve creating a maintenance schedule, implementing asset management policies, and conducting periodic audits.
Asset Retirement/Disposal:
When an asset reaches the end of its useful life or is no longer needed, it is retired or disposed of properly. This may involve data sanitization to remove sensitive information, recycling hardware components, or transferring software licenses.
Reporting and Analysis:
IT asset management processes generate reports and analytics to provide insights into asset utilization, costs, compliance, and other key metrics. This information helps decision-makers optimize asset usage, plan for future investments, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Continuous Improvement:
The IT asset management process is an ongoing cycle of improvement. Feedback and data collected throughout the process are used to identify areas for improvement, refine policies and procedures, and enhance overall efficiency and effectiveness.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively manage their IT assets, optimize resource allocation, reduce costs, ensure compliance, and minimize security risks associated with IT infrastructure and software.
Benefits of IT Asset Management
Efficient management of IT assets (ITAM) can greatly assist organizations in making better business decisions. Some of the key advantages are as follows:
Centralized Asset Database/Inventory:
Managing assets becomes challenging when they are scattered across different locations. This can lead to inaccuracies, disorder, inefficiencies, and subpar business decisions. Having a single source of reliable information makes it easier and more efficient to track assets. It allows organizations to identify assets that need to be disposed of, upgraded, or optimized for maximum productivity.
Optimized Asset Utilization:
IT asset management facilitates efficient resource utilization, risk mitigation, waste reduction, and cost savings. By implementing an ITAM process, organizations gain real-time data on the status of their assets and can make informed decisions regarding their usage.
Software License Compliance:
Organizations that use third-party software licenses often undergo software audits conducted by providers to ensure compliance with license terms and conditions. Failure to comply can result in significant fines. Therefore, organizations employ ITAM software to automatically monitor software installations across their computer networks, ensuring adherence to relevant license agreements.
Informed Decision-Making:
ITAM data contributes to evaluating previous purchases and deployments, which in turn informs subsequent actions. ITAM enhances the procurement of IT assets and improves business processes.
IT Asset Management Software
As an organization’s IT assets expand, manual, paper-based, or spreadsheet systems become cumbersome for their management. IT Asset Management (ITAM) software serves as a centralized application for lifecycle management and tracking of assets.
Features of ITAM Software
IT asset management software solutions typically encompass features that provide organizations with better control over their IT environment and enable asset tracking both on-premises and in the cloud. These features include:
Automated detection:
Most IT asset management systems, including Ivanti Neurons ITAM, automatically detect all hardware and software installed across an organization’s computer network.
License management:
ITAM software stores information about IT asset licenses. This information is cross-referenced with inventory data to alert the organization if it is under-licensed and at risk of violating license agreements or over-licensed, acquiring software that is underutilized or not used at all. This functionality also tracks license agreement expiration dates and provides appropriate notifications.
Version and patch management:
The release of new software patches and versions is monitored by ServiceNow Asset Management software, which ensures that an organization’s computers are safe, current, and operating at peak efficiency.
Request management:
Some ITAM software allows tracking of all IT asset requests and enables organizations to define asset request workflows. It evaluates license requirements for these assets and manages the acquisition and deployment process.
Inventory management:
ITAM tools maintain records of all assets utilized by an organization. The inventory includes asset details such as name, license agreement type, and version.
Configuration management database (CMDB):
The CMDB serves as a centralized database storing information about an organization’s IT assets and their relationships.
Fixed asset management:
Most ITAM tools include a dedicated repository for managing fixed asset data, primarily comprising hardware.
Digital asset management:
This feature of ITAM software involves managing digital rights and rich media, such as multimedia content (e.g., videos, music, and photos).
Factors to Consider When Choosing ITAM Software or Asset Management Solution
When choosing ITAM (IT Asset Management) software or an Asset Management Solution, there are several factors to consider to ensure you make an informed decision. Here are some key factors to take into account:
Functionalities:
Assess the specific features and functionalities offered by the ITAM software. Determine whether it meets your organization’s requirements, such as inventory tracking, license management, software deployment, hardware lifecycle management, contract management, and reporting capabilities.
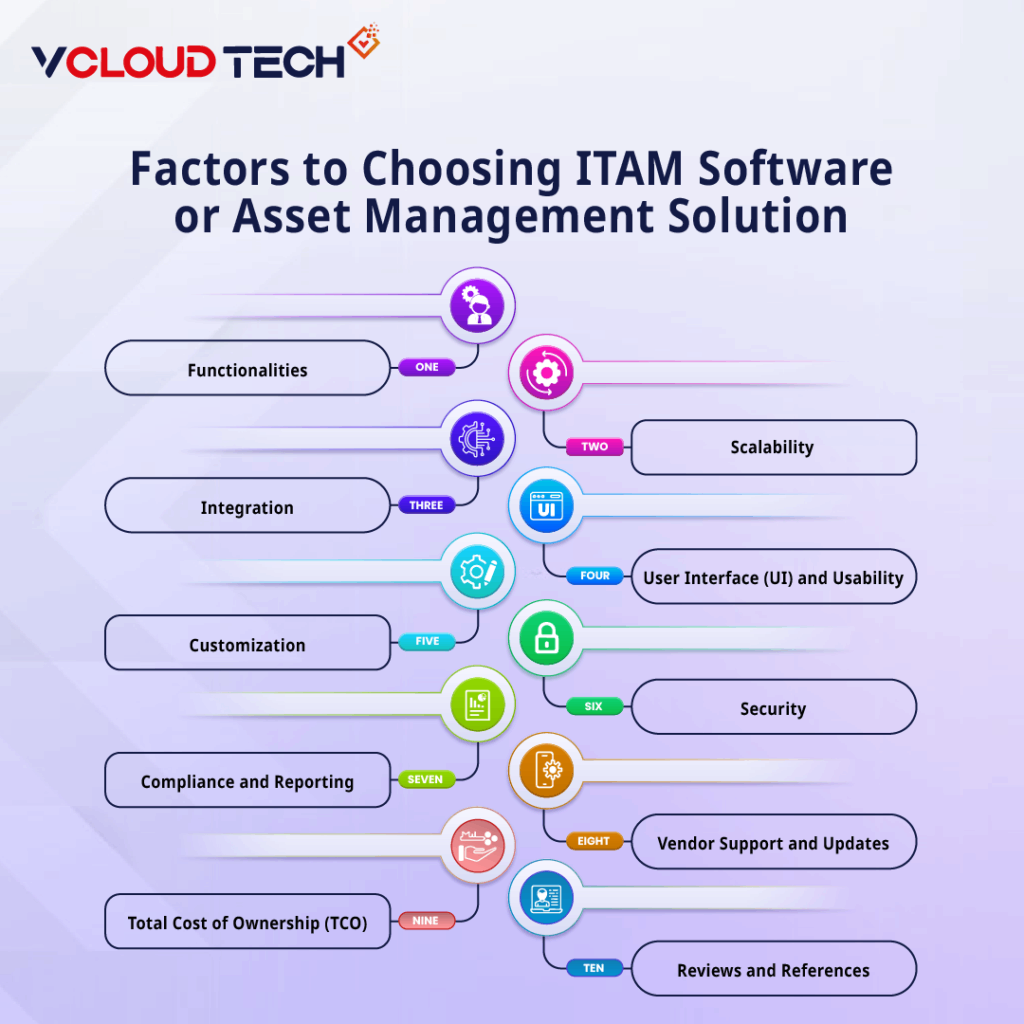
Scalability:
Consider the scalability of the software. Ensure that it can accommodate your organization’s current asset inventory size and has the ability to handle future growth.
Integration:
Evaluate the software’s compatibility with your existing IT infrastructure. Determine if it can integrate with other systems, such as IT service management (ITSM) tools, procurement systems, and financial systems. Seamless integration can streamline processes and improve efficiency.
User Interface (UI) and Usability:
A user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation are essential for effective asset management. Test the software’s usability to ensure that it is easy to use and understand. A well-designed UI can reduce training time and enhance productivity.
Customization:
Consider the level of customization options available. Every organization has unique requirements and workflows, so the ability to tailor the software to your specific needs can significantly improve its effectiveness.
Security:
ITAM software deals with sensitive information, including software licenses, hardware inventory, and vendor contracts. Ensure that the software has robust security measures in place to protect your data from unauthorized access or breaches.
Compliance and Reporting:
Check if the software provides features to help you maintain compliance with relevant regulations and licensing agreements. It should offer reporting capabilities that allow you to generate accurate and detailed reports for audits or management purposes.
Vendor Support and Updates:
Evaluate the reputation and track record of the software vendor. Look for a vendor that provides regular updates, bug fixes, and responsive customer support. Reliable vendor support ensures that any issues or questions can be addressed promptly.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Consider the upfront costs, licensing fees, ongoing maintenance expenses, and any additional charges associated with the software. Assess the long-term value and ROI (Return on Investment) the solution can provide.
Reviews and References:
Research user reviews and seek references from organizations that have used the ITAM software. Feedback from other users can provide insights into the software’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall satisfaction.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing an ITAM software or asset management solution that best aligns with your organization’s needs and goals.
IT Asset Management (ITAM) vs. IT Service Management (ITSM)
Here’s a comparison table between IT Asset Management (ITAM) and IT Service Management (ITSM):
| Factor | IT Asset Management (ITAM) | IT Service Management (ITSM) |
| Focus | Manages and tracks IT assets throughout their lifecycle, including procurement, inventory, maintenance, and disposal. | Focuses on delivering and managing IT services to meet the needs of end users and the organization. |
| Scope | Primarily deals with the physical and virtual assets in an organization’s IT infrastructure, such as hardware, software, licenses, and contracts. | Covers a broader range of activities including incident management, problem management, change management, service desk operations, and service level management. |
| Goal | Optimizes the utilization, availability, and cost of IT assets, ensuring compliance with licensing agreements and regulatory requirements. | Enhances the delivery, quality, and efficiency of IT services, meeting customer expectations and aligning with business objectives. |
| Processes | Asset procurement, inventory management, software license management, hardware maintenance, asset disposal, and contract management. | Incident management, problem management, change management, service request management, service catalog management, and service level management. |
| Benefits | Improved asset visibility, reduced costs through effective asset utilization, enhanced compliance, optimized software license usage, and streamlined procurement processes. | Improved service quality, reduced downtime through efficient incident and problem management, better change control, enhanced user satisfaction, and improved alignment of IT with business needs. |
| Key Tools | Asset discovery and inventory tools, software license management systems, contract management software, and asset lifecycle management solutions. | IT service desk software, incident management tools, problem management software, change management systems, service catalog software, and service level management tools. |
While ITAM and ITSM have distinct focuses and objectives, they are complementary and often work together to ensure effective IT operations within an organization. ITAM provides the foundation for managing IT assets, while IT Service Management (ITSM) focuses on delivering and maintaining quality IT services.
Stages of an IT asset lifecycle
The lifecycle of an IT asset typically consists of the following stages:
Planning and Procurement:
In this stage, organizations assess their IT needs, plan for future requirements, and determine the assets to be acquired. This includes defining specifications, conducting vendor evaluations, negotiating contracts, and making procurement decisions.
Acquisition and Deployment:
Once the Data Assets are procured, they are acquired and deployed within the organization. This involves physical installation, configuration, and integration of hardware and software components. Asset tags or unique identifiers may be assigned to track and identify each asset.
Utilization and Operation:
During this stage, the IT assets are actively used in the organization’s operations. Users or departments utilize the assets to perform their tasks, whether it’s using computers, accessing software applications, or utilizing networking equipment.
Maintenance and Support:
Regular maintenance activities are performed to ensure the assets continue to operate optimally. This includes applying software updates, performing hardware repairs or replacements, managing licenses, and providing technical support to address issues or concerns.
Upgrade or Enhancement:
Over time, IT assets may require upgrades or enhancements to keep up with evolving technology, security requirements, or business needs. This stage involves assessing the asset’s performance, compatibility with new systems, and evaluating the benefits of upgrading or enhancing the asset.
Asset Replacement:
In some cases, assets may be replaced with newer models or technologies to improve efficiency, productivity, or cost-effectiveness. This stage involves planning for asset replacement, determining the best time for replacement, and managing the transition from the old asset to the new one.
Throughout these stages, IT asset management practices, including tracking, documentation, and reporting, play a vital role. They help organizations maintain visibility and control over their assets, optimize asset utilization, manage costs, ensure compliance, and make informed decisions regarding the lifecycle management of IT assets.
Reach out to us and book a Free Consultation with vCloud Tech or chat with one of our representatives. Connect with us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn for more information.









