The zero-trust security model gained significant momentum throughout 2022, receiving substantial backing from government entities and businesses as a fundamental component of their IT strategies. With the continual increase in ransomware attacks and data breaches, we can anticipate a continuation of this trend in the current year.
In safeguarding sensitive enterprise data, zero-trust security significantly surpasses perimeter-based security measures. According to Research from Nemertes, companies achieving the most favorable cybersecurity outcomes are 137% more inclined to adopt a zero-trust approach. However, for organizations to effectively reinforce their IT infrastructure, they must ensure that implementing zero trust is seamless.
Additionally, enterprises must undertake a thorough data discovery initiative and undergo a comprehensive Cybersecurity assessment before devising a strategy for implementing zero trust. After all, IT teams must clearly understand the data they intend to safeguard and its specific locations. Although this procedure may appear straightforward, it presents significant challenges. But before we get ahead of ourselves, let’s define it.
What Is Zero-Trust Security?
The Zero-Trust Security model is a strategy employed to safeguard an organization. It is rooted in the principle that no individual or device should be automatically considered trustworthy, even if it is already within the organization’s network. The zero-trust approach eliminates assumed trust by implementing rigorous identity Authentication and Authorization procedures across the entire network rather than solely at a designated trusted perimeter. In this framework, each request to access resources is treated as originating from an untrusted source until it undergoes inspection, authentication, and validation.
The concept of zero trust was initially introduced by Forrester Research analyst John Kindervag in 2010. It represented a departure from conventional IT security models, which primarily concentrate on securing access at the network perimeter and assume that everything inside is inherently trustworthy.
Regrettably, the traditional approach offers limited protection once attackers enter a network. Once inside, attackers can move freely and attempt to expand their reach to valuable data and assets, a tactic known as lateral movement. This issue is even more pronounced in contemporary IT environments, where resources and data are widely dispersed, making it challenging to enforce security controls from a single point. Adopting a zero-trust approach can assist organizations in enhancing the security of their IT environment and mitigating or preventing cyberattacks.
How Does Zero Trust Work?
The zero-trust approach eliminates the notion of a trusted network boundary. It assumes that any user or service seeking access poses a potential security threat, regardless of their location within your network or prior connection history. While some may simplify the concept of zero trust as “trust no one and nothing” or “never trust, always verify,” these characterizations are oversimplified. The core idea behind Zero Trust is that placing trust in anyone or anything, even the foundational components of an interconnected system introduces significant security risks. Trust established and continuously validated through dynamic, context-aware security policies and technological mechanisms.
This approach employs micro-segmentation, using fine-grained policy controls to segment the network into smaller units and isolate workloads. These policies are based on contextual factors such as identity, location, device, the type of content being accessed, and the specific application in use. The guidelines are dynamic and regularly re-evaluated and adjusted as the context evolves.
By default, data and resources remain inaccessible, and connections are only granted after rigorous authentication and authorization processes. This thorough process applies to every user and connected endpoint, with continuous authentication of identities. Additionally, all network traffic is meticulously logged, monitored, and analyzed for any signs of potential compromise.
Benefits Of Using The Zero-Trust Model
Zero-trust security brings about several key advantages:
Increased Visibility:
Zero trust necessitates that businesses clearly understand where their assets are situated and continuously monitor who or what identities are accessing resources, along with how they are doing so. That enhances visibility and context surrounding network traffic, asset inventory, and risk management.
Limitation of Breach Impact:
By granting least-privilege access to identities, Zero Trust Solutions helps restrict the potential damage in case of a breach. That empowers security teams to respond swiftly and mitigate attacks, reducing the risk of further exposure.
Access Control in Modern IT Environments:
Zero-trust architecture bases security policies on identity and associates them with specific workloads. That enables security measures to stay closely aligned with the assets being safeguarded, regardless of the particular environment in which they operate.

Consistency and Adaptability in Security:
In zero-trust models, security policies are centrally managed and leverage automation to facilitate migrating and updating policies based on contextual information. That makes security more agile and scalable while relieving the administrative burden.
Reduced Attack Surface and Risk:
Zero trust isolates traffic and establishes network segments that hinder lateral movement and prevent potential infections from spreading to critical resources. Suspicious activity scrutinize, and identities can be re-verified through policies and controls, diminishing the likelihood of a successful breach.
Continuous Compliance:
Zero trust mandates logging and evaluating all traffic and requests while imposing strict access controls on resources. That creates a comprehensive audit trail in the event of a breach and simplifies the process of demonstrating compliance with data privacy requirements and standards, affirming that all feasible measures have been taken.
The Three Zero-Trust Concepts
The zero-trust model encompasses various implementations today, including Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Zero-Trust Architecture (ZTA), and Zero-Trust Edge (ZTE). However, they all have a foundation built upon the same fundamental concepts.
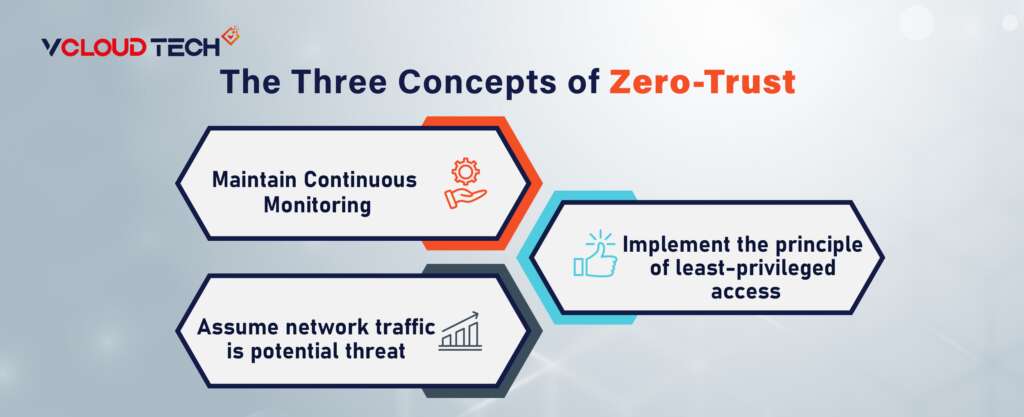
Here are the three core principles that underpin the zero-trust model:
Assume that all network traffic is a potential threat at all times.
Zero trust adopts the perspective that every user is regarded as a potential threat, and threats can originate from anywhere, whether inside or outside the network. Consequently, any traffic lacking explicit authorization is automatically denied access. Each device, user, and Zero-Trust Network flow is subject to ongoing authentication, license, and validation when requesting access.
Implement the principle of least-privileged access.
Zero-trust security strategies adhere to the principle of granting the least privilege necessary—providing users and devices with only the minimum rights and access required to perform their tasks without compromising their ability to complete them. This approach limits attackers’ ability to move laterally to more critical resources if they compromise an account or device.
Maintain continuous monitoring
The Zero-Trust Model advocates for perpetual monitoring, analysis, and network activity management. This constant vigilance allows for real-time awareness of entities attempting to access resources. It assists in identifying potential threats, ongoing security incidents, and any unusual or abnormal activities that warrant investigation.
These zero-trust principles, originally articulated by Forrester, align closely with the zero-trust framework developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). We recommend referring to NIST’s framework for practical guidance on implementing a zero-trust security model within your organization.
Why Use a Zero-Trust Model?
Many of today’s significant data breaches do not solely result from attackers breaching the network perimeter. The proliferation of cloud computing and remote workforces has challenged organizations to safeguard increasingly dispersed environments with porous boundaries. Zero-Trust Data Security is now generated, stored, and shared across numerous services, devices, applications, and individuals, accessible from anywhere globally.
A notable number of threat actors have realized that exploiting vulnerabilities and gaps within hybrid cloud environments can be a lucrative endeavor. Recently, major breaches have often occurred due to compromised accounts resulting from social engineering and other advanced techniques, accidental or deliberate insider threats, and third-party vendors’ less stringent security practices.
Security teams have understood that threats are as likely to emerge within the network as external sources.
Organizations have attempted to implement defense-in-depth security measures to provide redundancies and backup security in case one layer fails. However, this approach can be costly and complex to establish, manage, and sustain, especially considering the constant need for adjustments and modifications as new systems, individuals, services, and devices are introduced.
Zero trust incorporates defense-in-depth strategies, but its primary objective is to minimize the attack surface and construct inherently secure environments without the necessity of identifying and mitigating every potential threat individually. The emphasis is on preventing access to critical assets and thwarting lateral movement by attackers within the network in real-time. Zero trust offers a unified security approach that delivers comprehensive, adaptable protection for distributed environments while permitting secure access.
Challenges Of Using The Zero-Trust Model
Indeed, the zero-trust approach offers significant benefits. In addition, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. The transition to zero trust can be a lengthy process that demands careful planning. Here are some of the most notable challenges associated with implementing zero trust:
Consistency:
Achieving the full potential of zero trust requires consistent execution of the strategy. Organizations must implement changes gradually as they move away from traditional security solutions. It’s crucial to ensure no security gaps during this transitional period.
Productivity Impact:
Zero trust introduces additional security steps into many workflows, potentially impacting productivity if not implemented thoughtfully. Striking the right balance between supporting work processes and maintaining a robust security posture is essential. If security measures become overly disruptive, individuals may attempt to bypass them, inadvertently creating vulnerabilities.

Insider Threats:
While zero trust can help mitigate insider threats by enforcing least-privilege access, it is not a complete solution. Attackers can still find ways to gain access by stealing credentials through phishing or tricking individuals into sharing sensitive information. Additionally, there may be malicious insiders intent on abusing their privileges. Organizations need to implement comprehensive monitoring and anomaly detection mechanisms to address insider threats across their entire environment effectively.
Policy and Architecture Maintenance:
Businesses continually evolve, meaning zero-trust policies and permission structures must evolve and adapt. Zero-trust models rely on well-defined policies and effective policy administration, necessitating proactive maintenance and configuration updates to prevent security breaches.
Wrapping Up the Discussion:
The future of cybersecurity is here. That’s the Zero Trust security model. The perimeter-based, reactive methods that served as the foundation of old traditional security should become a thing of the past. Businesses and governments must proactively adopt Zero Trust now to confidently deliver a cybersecurity-secure future to their customers, partners, employees, and citizens. It’s time to prioritize security to protect, detect, and mitigate modern threats. Only this new generation of Zero Trust security framework provides network visibility and constant monitoring, validating every access request and granting access only if specific parameters are met, allowing for dynamic enable context-based trust.
Reach out to us and book a Free Consultation with vCloud Tech or chat with one of our representatives. Connect with us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn for more information.









